Types of Version Control Systems
Types of Version Control Systems
Centralized Version Control System (CVCS): A single and “central†server acts as the main data storage unit for every version of the code.
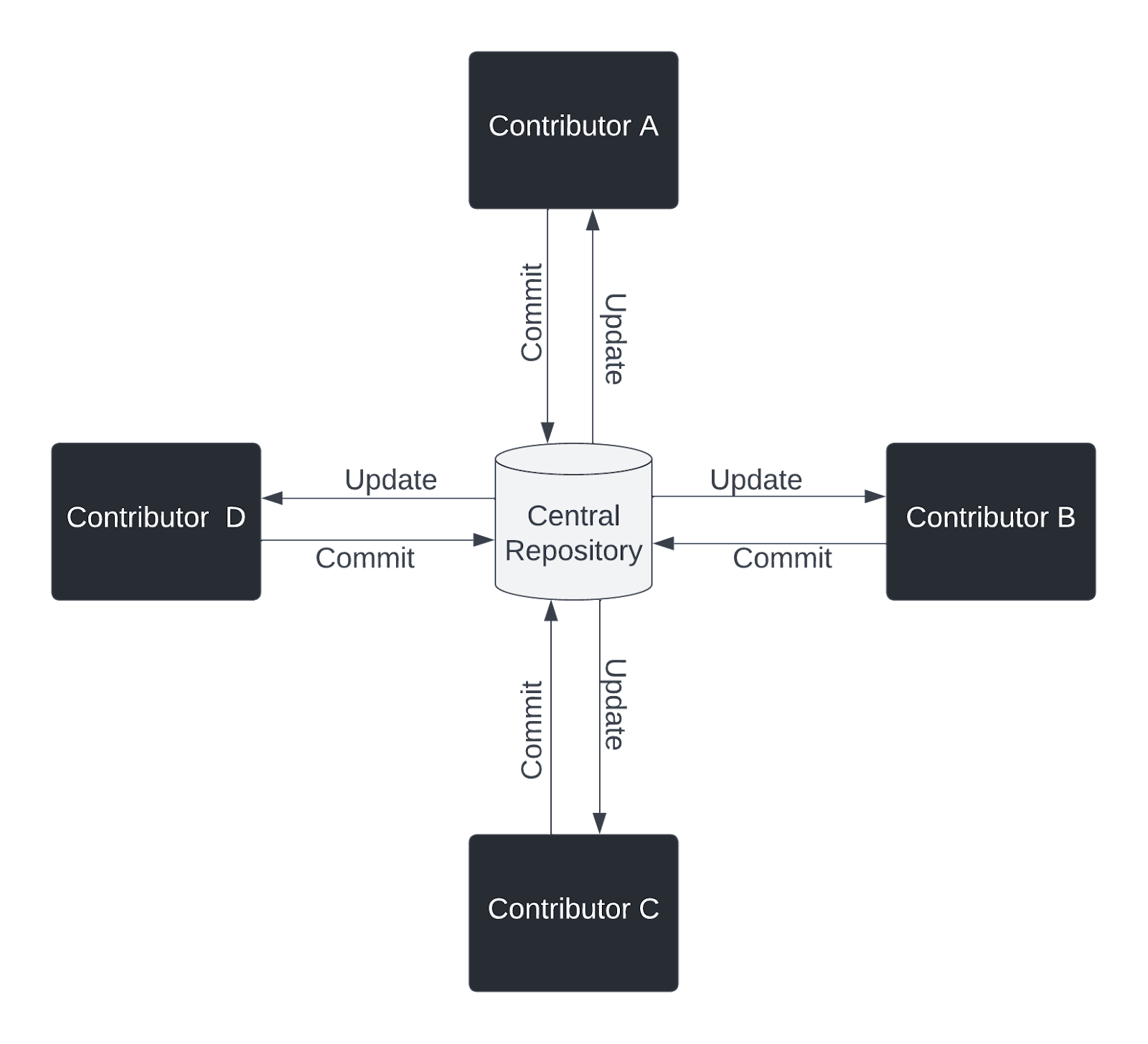
Examples include: Concurrent Versions System (CVS), Apache Subversion (SVN), Polytron Version Control System (PVCS), IBM Rational ClearCase, CADES, and Perforce Helix.
Distributed Version Control System (DVCS): The data storage unit for every version of the code is mirrored on both the “central†server and developer’s local computer.
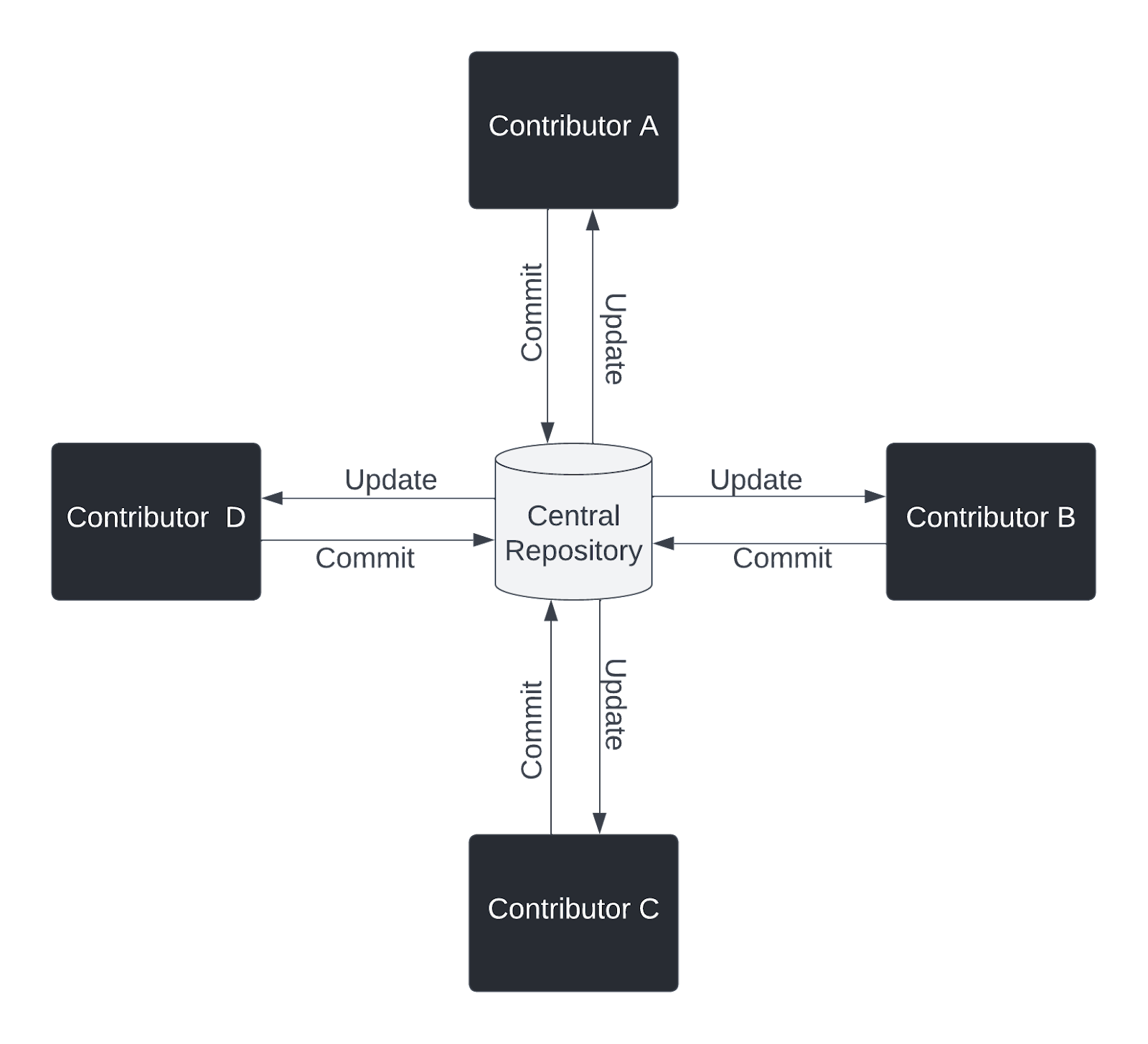
This enables branching, merging, increased speed, offline capabilities, and distributed backups. Examples include: Git, Bazaar, Plastic SCM, Darcs, Mercurial, Fossil, and BitKeeper.
